A New Wave of Clean Energy: Turning Seawater into Green Hydrogen
The Hydrogen Dilemma
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, and when used as a fuel, its only byproduct is water. This makes it an incredibly attractive clean energy source. However, the vast majority of hydrogen produced today is “grey hydrogen,” made from natural gas in a process that releases large amounts of carbon dioxide.
“Green hydrogen” is the ideal alternative. It’s produced by splitting water (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen using a process called electrolysis, powered by renewable energy. The problem? This process requires highly purified, fresh water, a resource that is already scarce in many parts of the world.
A Breakthrough from the Ocean
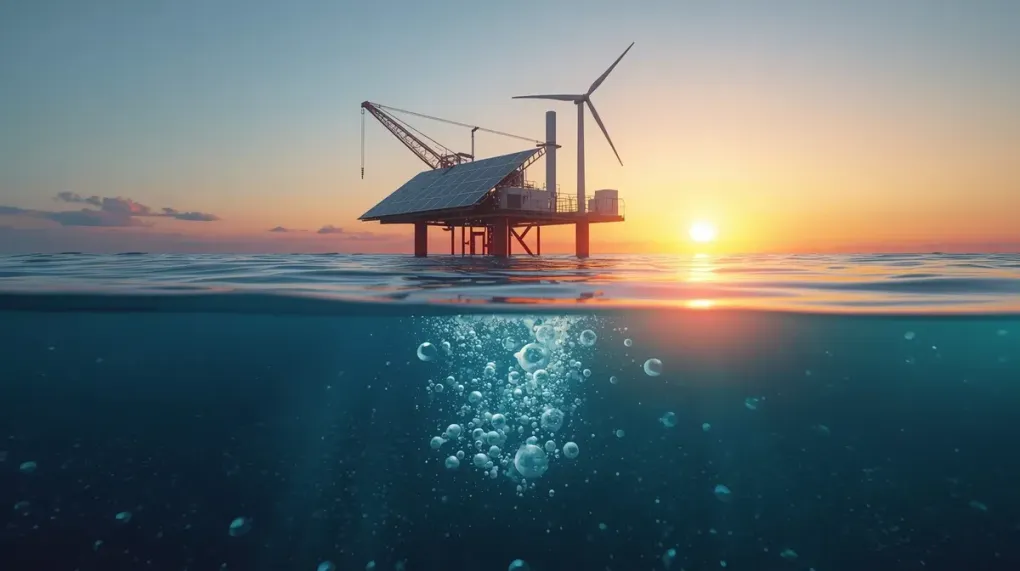
But what if we could use the most abundant water source on the planet: seawater? A groundbreaking new technology is doing just that. Researchers have developed a method to produce green hydrogen directly from seawater, without the need for desalination or purification.
This is a significant leap forward. Traditional electrolysis systems get clogged and corrode when exposed to the salt and other impurities in seawater. This new approach uses a specially designed electrolyzer that can handle the harsh marine environment, opening up a vast and previously untapped resource for clean energy production.
How it Works
The innovative system uses a catalyst that is resistant to the corrosive effects of salt. By running electricity from a renewable source (like a solar panel or wind turbine) through the seawater, the system splits the water molecules, releasing hydrogen gas while also creating a byproduct that can be used for carbon capture.
This means the technology not only produces a clean fuel but also has the potential to permanently store CO2, effectively creating a carbon-negative energy source. It’s a two-for-one solution in the fight against climate change.
The Future of Fuel?
The potential is immense. Imagine offshore platforms that use wind or solar power to generate hydrogen from the ocean itself. This hydrogen could then be used to power ships, generate electricity for coastal cities, or be transported inland to fuel vehicles and heavy industry.
This technology is still in its early stages, but it represents a paradigm shift in how we think about clean energy. By unlocking the potential of seawater, we could create a truly sustainable and virtually limitless supply of green hydrogen.
It’s a powerful reminder that the solutions to our biggest challenges can often be found in the natural world. The ocean, which covers more than 70% of our planet, may hold the key to a clean energy future.